Table of Contents[Hide][Show]
For diabetes, omega 3 fats may help reduce insulin resistance, improve blood sugar levels, boost heart health, and more.
Read on as we explore what it is, how it works in your body, the best food sources and whether supplements can help.

What is an Omega 3?
Generally speaking, an omega 3 fat is a type of fat touted for its numerous health benefits. But to really understand what an omega 3 fat is, let’s briefly review fat as a whole.
The two main categories of fat are saturated and unsaturated fat. Unsaturated fat can be broken down into further categories, which include monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fat.
An omega 3 fat is a specific type of polyunsaturated fat.
Another well known type of polyunsaturated fat is an omega 6, and while this isn’t the focus of our discussion, know that omega 6 fatty acids do the opposite of everything an omega 3 fatty acid does in terms of your health.
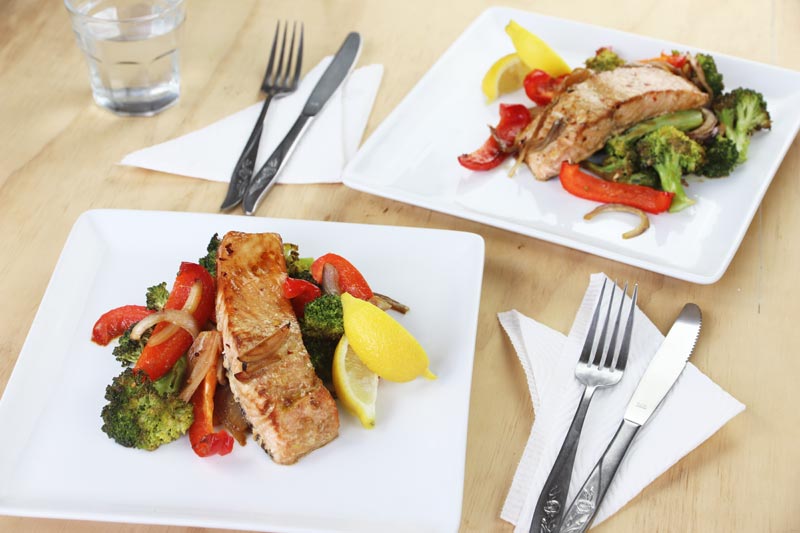
Omega 3 fats can further be classified as DHA or EPA – these are the “primary source” that your body can utilize directly.
There is a third type of omega 3 called ALA, which is a “secondary source.” ALA must be converted into DHA or EPA to be optimally utilized by your body. Most sources of omega 3 will contain a mixture of DHA, and EPA, and sometimes ALA.
How Do Omega 3 Fats Work?
The reason omega 3 fats are so healthy is because of their ability to reduce inflammation.
All types of fat become incorporated into your cell membrane. Your cell membrane is the barrier that surrounds each of your trillions of cells, and to an extent you need a balance of different types of fat in your cell membrane as each serves a different purpose.
However, when there is a higher percentage of omega 3 fats present we see several positive things occur.
Cells are healthier: Omega 3’s help keep the cell membrane flexible. This is important because a flexible membrane allows beneficial nutrients to enter your cell, allows enzymes to embed in the membrane and trigger necessary reactions, yet is still able to act as a barrier to harmful particles that may be floating around.
Reduce inflammation: When omega 3’s bind to receptors in your cell membrane there is a cascade of reactions that occur to help reduce inflammation.
Some of these reactions help to produce anti-inflammatory molecules such as eicosanoids and resolvins while other reactions decrease the number of pro-inflammatory molecules from being produced. The end result is an overall decrease in inflammation.
Boost heart health: Another added benefit of omega 3 fats are their cardioprotective benefits as they inhibit blood from “sticking” together as much; this can allow blood to flow more smoothly through your veins.
Prevent inflammatory molecules: And remember those omega 6 fats? They are notorious for increasing inflammatory molecules, which wreak havoc on your body when left unchecked.
Hence, the more you can increase your omega 3 intake and decrease your omega 6 intake the better off you will be. But don’t take our word for it, let’s see what the research has to say about omega 3’s and your health.
Research on Omega 3 for Diabetes
May Improve Glucose Control and insulin Sensitivity
One study found that when moderately obese individuals with diabetes followed a high protein, low glycemic index diet, and supplemented with omega 3, there was a decrease in HbA1c from 7.9% to 7.3% after 24 weeks of intervention. Additionally, the high protein, low glycemic index and omega 3 supplementation decreased waist circumference and inflammation.
Another similar study assigned individuals with diabetes to one of four diets:
- high carb
- low carb
- omega 3 supplemented
- or low carb plus omega 3 supplemented
Those individuals who were assigned to a omega 3 group received 6 grams of fish oil per day. With the exception of the high carb group, all other interventions saw a decrease in HbA1c and fasting blood sugar. However those in the low carb plus omega 3 group saw the largest improvement in glucose control.
A 2014 study found 4 grams per day of omega 3 fat successfully improved insulin sensitivity in those individuals with diabetes.
Likewise, omega 3 supplementation was found to be more effective in improving insulin sensitivity than diet alone in postmenopausal women with metabolic syndrome. After omega 3 supplementation, the intervention group also achieved a greater reduction in blood pressure, triglyceride concentrations, and inflammatory markers.
A 2015 meta-analysis noted mixed results when it came to omega 3 supplements and diabetes control. But researchers did note that early intervention is a crucial component of omega 3 supplementation for glucose control. This suggests individuals may benefit more if action is taken early.
May Improve Cardiovascular Function
A 2017 study demonstrated omega 3 supplementation is an effective intervention for high triglyceride levels. Those individuals taking 2 grams of omega 3 daily saw triglycerides lower from 144.83 mg/dl to 86 mg/dL (a 58.83 reduction), compared to those only taking 1 gram of omega 3 daily saw a smaller 43 mg/dL decrease; both doses were more effective than the placebo.
Researchers found that 1 gram of omega 3 supplementation was effective for lowering blood pressure after 8 weeks of intervention.
Another study suggests omega 3 fats helps improve blood flow in both large and small blood vessels of the body. The researchers found 2 grams of DHA/EPA omega 3 supplementation significantly improved blood flow and decreased inflammatory markers in patients with metabolic syndrome.
May Improve Renal Function
Researchers examined 344 patients with diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and a history of omega 3 supplementation and determined omega 3 supplementation may help maintain renal function. Patients taking higher doses (>4 grams/day) had greater preservation of renal function compared to those taking lower doses.
Another 2011 study of healthy individuals also observed a correlation between omega 3 intake and chronic kidney disease. Participants with a higher intake of omega 3 had a 31% reduced risk of developing kidney disease compared to those in the lowest intake group.
May Improve Brain Function
People with diabetes are at a 50-65% increased risk of developing dementia as a result of metabolic disturbances and insulin resistance. Interestingly, omega 3 fat is thought to improve brain function by strengthening white matter integrity and volume, as well as vascular blood flow.
One study conducted in hypertensive individuals found that omega 3 supplementation increased blood flow response in the brain by as much as 26%.
While another analysis of 266 participants suggests higher blood levels of DHA (one type of omega 3) results in a 65% reduced risk of developing dementia.
While more research is needed in this area, many animals studies have observed an improvement in learning, memory and anxiety after administration of omega 3 fats in diabetic rats.
May help with Prevention
For those reading this who are not diabetic, rest assured that omega 3 intake has also been associated with reducing your risk of developing diabetes.
A 2014 study from the American Diabetes Association followed 2,121 men for 20 years and concluded that those men who had the highest EPA/ DHA levels had a 33% lower risk of developing diabetes compared to those in the lowest group.
Djoussé and colleagues found similar preventive properties for EPA/DHA levels, and also noted a 43% lower risk of diabetes when the highest to lowest groups of ALA were compared.
Please pin, tweet or share; then keep reading – thanks!

Omega 3 Food Sources
Remember, sources of omega 3 can either be classified as “primary sources” or “secondary sources.”
Omega 3’s are not readily available in a standard Western diet, but you can increase your omega 3 intake by including fish in your diet two or three times per week.
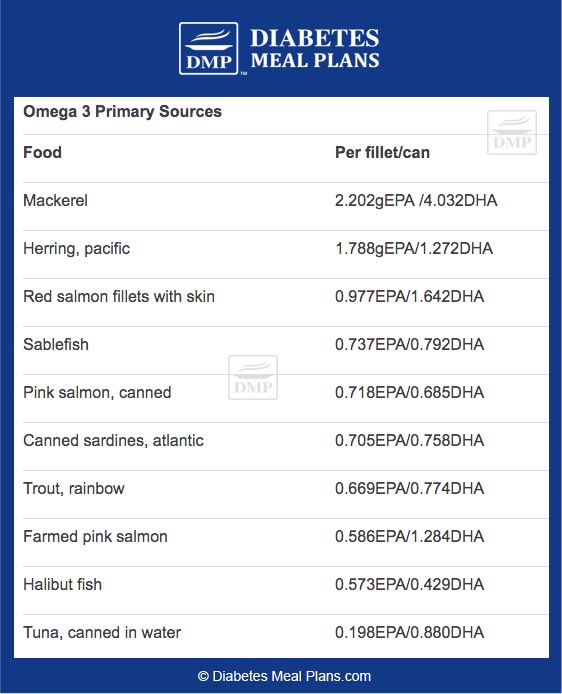
For those who do not like fish, there are a few secondary sources of omega 3 that we encourage you to consume regularly.
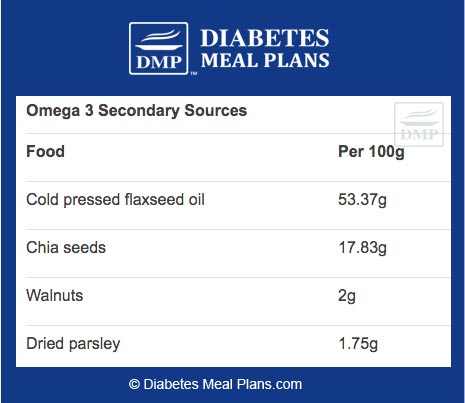
Your best bet is to consume a variety of both primary and secondary sources!
What About Omega 3 Supplements?
Fish oil has gained much popularity over the years, and probably for good reason.
Most people do not consume nearly enough omega 3 fats. The optimal ratio of omega 6 to omega 3 in your diet should be around 4 (omega 6): 1 (omega 3), however the standard Western diet is closer to 25:1.
We eat outrageously too many omega 6 fats!!
One of the easiest ways to improve your ratio is to consider taking an omega 3 supplement. It’s also beneficial to reduce your omega 6 intake by limiting foods such as margarine and vegetable oils such as corn, safflower, soybean, grapeseed, peanut oil, and sunflower oil. Grains and grain-based foods also contain high amounts of omega 6.
The recommended dosage for supplementation ranges from 2-4g of EPA and DHA daily.

While there are different sources of fish oil available, cod liver oil is the most popular omega 3 supplement. For a vegetarian source or if you can’t tolerate fish oils, then choose flaxseed oil instead.
Supplements come in liquid and gel capsule, both of which should be stored in the refrigerator. Although the liquid may be harder for some people to swallow, it’s also less likely to lead to belching or reflux afterwards.
Fish oil can affect your body’s ability to clot blood, which can interfere with drugs such as aspirin or Coumadin. Check with your doctor prior to starting any omega 3 supplements
Conclusion
Without a doubt omega 3 fats are one of the healthiest fats you can consume in your diet!
Foods such as fish, flaxseed, and walnuts are great to include on a regular basis, and when paired with a low carb diet are sure to help improve blood sugar levels.
Omega 3 fats help reduce inflammation, which can make controlling chronic diseases such as diabetes easier. Unfortunately, most people do not consume enough omega 3 fats in their diet.
Make it a point to include fish two to three times per week, and consider speaking with your doctor about whether a fish oil supplement may be right for you.
Please pin, tweet or share this info to help others – thanks!


Cathy
As little as 2.8 Oz. Of wild caught salmon for supper reduces my fasting blood glucose on the next morning by 15-20 points. A 3-day sardine fast does the same thing, and sardines have lower levels of mercury.
Robert Charles Rice
Carry on! I like it!
SherryElaine Painter-Burns
Thank you for the information I seem to do everything correct but don’t sleep have a lot of emotional stress and crave sweets like crazy I Am not exercising much because of arthritis and I have no company or away to go i am pretty much house bound.. I am do suffering from Psoriasis and need some one who knows how to treat this properly i am in an area where they treat it but not with the way they did in Austin Texas when I first got it.. I have betaling fish oil and supplements for years.. i feel do defeated..I am 72 and and don’t see much time or future ..
Emily - Dietitian (MS, RD)
Just remember, diabetes is a bit of a game and you just have to figure out the right pieces to your treatment plan. You CAN gain control.
You may have trouble doing intense physical activity, but could you start with some stretching while watching TV? This would at least get your body moving a little, and it may help with your arthritis pain and help you sleep better! Try to avoid keeping ANY sweets in your house so that it is not a trigger, instead keep lots of healthy snacks on hand for you to quickly grab.
Shirline
Great information much appreciated. Education in all areas and on all topics are of utmost importance and should be given freely, as you have done. Thank you.
Emily - Dietitian (MS, RD)
Thank you for the kind words, Shirline.