Table of Contents[Hide][Show]
We hear a lot of hype about herbal remedies and their miraculous powers to treat every ailment, including the various benefits offered for the treatment of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
And while there is lots of hype, we’re here today to explore some of the science behind these remedies to help ensure you can achieve the best outcomes if you choose to use them.

Before Jumping in Head First
Although many herbal remedies can be combined, Sarah Outlaw (Clinical Herbalist & Nutritionist) recommends that you introduce them one at a time so you can be aware of any sensitivities that may occur.
“Some herbs interact with medications so it is important to check for contraindications when considering any herbal supplementation,” she says.
Sarah also advises that tinctures and powder form (often found in supplements) are more potent herbals, that are often used for clinical outcomes. But if you use loose herbs in teas in larger quantities and steep them longer, you can also enjoy their incredible medicinal benefits.
DISCLAIMER
Please note that this information is not an endorsement for any of these herbs and remedies. We are simply sharing the research surrounding it. You should always discuss supplementation with your doctor or a trained health professional.
Cinnamon
Cinnamon is both a delicious spice and a powerful anti-inflammatory agent that has the potential to improve type 2 diabetes. In fact, one scientific study ranked cinnamon as one of the top anti-inflammatory foods out of 115 foods tested!
Cinnamon is also rich in natural antioxidant compounds. And this potent combination of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties makes cinnamon a disease-fighting superfood!
Here are some of the ways cinnamon may help support better health with diabetes and prediabetes:
May Support Improved Blood Sugar
One study found that taking 3 grams of cinnamon daily for an 8 week period reduced fasting blood glucose levels by 11.65 mg/dL (0.6 mmol/l).
Another study found that the same dose of cinnamon resulted in a 9.2% drop in fasting blood glucose, 12.8 mg/dL (0.7 mmol/l) and a reduction in A1C by 0.45%, after 8 weeks of supplementation.
May Improve Cholesterol and Body Weight
Cinnamon has been shown to have a positive impact on cholesterol levels and body weight.
For example, one study found that a dosage of 3 grams of cinnamon for 8 weeks resulted in a significant decrease in triglycerides (-15.38%) in a group of people with type 2 diabetes.
As a bonus, the diabetics taking cinnamon also experienced a decrease in BMI (-1.54%) and a decrease in overall body fat mass (-1.36%) by the end of the 8 week trial.
Try our Homemade Cinnamon Tea Recipe.

Turmeric
Turmeric is a popular spice that will add the perfect touch of smoky flavor and rich yellow-orange color to your next curry dish. But more than that, turmeric is famous for its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
The major bioactive compound in turmeric is curcumin. And when it comes to scientific evidence, curcumin exhibits some very impressive benefits.
May Lower Blood Glucose and A1C Levels
In studies, turmeric oil has been shown to inhibit the activity of certain enzymes (called alpha-glucosidase and alpha-amylase), which assists with lowered glucose and A1C levels in diabetic patients.
This same action was also seen in a 2016 clinical trial of type 2 diabetic patients. The patients who received a dose of 80 mg/day of curcumin for 3 months saw a 15.3 mg/dL (0.9 mmol/l) reduction in fasting blood glucose, as well as a drop in A1C of 0.28%.
In contrast, the placebo group didn’t see any benefits over the 3-month period. In fact, they actually experienced a rise in their A1C and fasting blood glucose levels.
May Lower Cholesterol Levels
It is unfortunate that type 2 diabetes can put you at risk for higher cholesterol levels and therefore, higher risk of heart disease, too.
Though fortunately, this is one area turmeric may help.
A 2017 review of multiple studies concluded that taking 1 to 4 grams of turmeric provides protection for patients at risk of heart disease by reducing triglycerides and LDL “bad” cholesterol. It is also considered relatively safe to take alongside conventional medications.
May Reduce Oxidative Stress
Free radicals are unstable molecules in the body that, if left unchecked, can do a lot of damage to your body on a cellular level, especially if there are too many of them running around. This is known as oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress is one of the major factors linked to insulin resistance, a metabolic disruption that is closely linked to the development of type 2 diabetes.
Thankfully, this is where antioxidants like those in turmeric step in to save the day!
Antioxidants combat free radicals to help reduce cellular damage and promote better health.
One study found that giving rats a turmeric supplement significantly reduced levels of oxidative stress markers in the blood and liver, with improvements in overall antioxidant status.
A clinical trial in patients with type 2 diabetes found that supplementing with curcumin at a dose of 1000 mg/day for 8 weeks, produced an increase in their total antioxidant capacity and greatly reduced their levels of oxidative stress.
Aloe Vera
The gel from the aloe vera plant has soothing properties that are well-known for their ability to heal sunburn and calm digestive distress.
However, aloe vera may also be a key player in improving the health of people with type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
May Improve Insulin Sensitivity and Metabolic Factors
A study on diabetic rats discovered that the administration of aloe vera reduced blood glucose, reduced insulin levels and improved the antioxidant glutathione. More than that, they found that aloe vera worked more effectively than the medication Glimiperide in stimulating and increasing insulin secretion.
How exactly does aloe vera reduce glucose and improve insulin levels?
Research suggests that aloe vera has potent anti-inflammatory capacity to downgrade several pro-inflammatory markers that cause havoc.
For instance, these pro-inflammatory molecules contribute to insulin resistance, and by suppressing them, the compounds in aloe vera may increase insulin sensitivity, which results in lower blood sugar and a better A1C.
Aloe vera may also improve various metabolic factors.
One study in prediabetic and newly diagnosed type 2 diabetic patients, found that, when compared to the placebo group, 8 weeks of aloe vera supplementation resulted in reduced fasting blood glucose, reduced total body weight, reduced fat mass, and reduced insulin levels.
Ginger
Ginger has been used for thousands of years as a natural treatment for nausea, body pain, and motion sickness, but it also has the potential to boost your metabolic and cardiovascular health.
May Lower Fasting Blood Glucose and A1C
A review of 9 clinical trials found that ginger intake significantly reduced fasting blood glucose levels by an average 14.93 mg/dL (0.8 mmol/l).
Another study reported similar results. The group of type 2 diabetic participants who received a ginger supplement of 3 g/day for 3 months had lower blood glucose levels by an average 19.41mg/dL (1.1 mmol/l), along with seeing an average 0.77% reduction in A1C levels, reduced insulin resistance, lower insulin levels, and a reduction in pro-inflammatory molecules.
May Optimize Cholesterol Levels
Low levels of “good” HDL cholesterol and high levels of lipids like triglycerides can be indicative of suboptimal cardiovascular health. But interestingly, natural compounds in ginger may be able to help
Studies have found that daily ginger intake is associated with lower levels of triglycerides and total cholesterol, along with improvements in levels of HDL “good” cholesterol!
Please pin, tweet or share; then keep reading.

Fenugreek
Fenugreek is another humble herb full of inflammation-fighting properties with proven blood-sugar lowering effects.
And amazingly, fenugreek may even prevent prediabetics from developing type 2 diabetes!
Let’s look a little closer.
May Improve Blood Sugar Control
A review of 10 clinical trials found that fenugreek supplementation produced an average 17.3 mg/dL (0.96 mmol/l) drop in fasting blood glucose, an average 39.4 mg/dL (2.19 mmol/l) decrease in 2 hour postload glucose, and a drop in A1C by 0.85%.
Another study found that when type 2 diabetic patients supplemented with 10 g/day of powdered fenugreek seeds for 8 weeks, they saw significantly reduced fasting blood glucose and A1c levels, decreased insulin resistance, and improved cholesterol and triglyceride levels.
In addition to its anti-inflammatory properties, researchers suggest fenugreek contains a plant compound called “GII” that acts as a glucose-lowering agent in the body. This compound is likely to be the major factor producing the lower blood sugar levels seen in the studies above.
May Help Prevent Prediabetes to Type 2 Diabetes
According to researchers, fenugreek may also be able to slow down the progression of prediabetes to the development of type 2 diabetes.
For example, a randomized trial conducted over a 3-year period, gave people with prediabetes 5 grams of fenugreek powder twice per day before meals and monitored their progression closely every 3 months for the duration of the 3 year trial.
The researchers found that, compared to the control group, the group taking daily fenugreek supplements had a significant reduction in fasting plasma glucose, postprandial glucose, improve insulin function, and lower LDL cholesterol.
But, the most impressive discovery was that the participants who weren’t given the fenugreek supplementation had a 4.2 times greater risk of developing diabetes!
Bitter Melon
True to its name, the taste of bitter melon is a little on the sour side. But even so, the health benefits are pretty sweet!
Bitter melon is equipped with 32 active phytochemicals that support health by minimizing systemic inflammation and battling free radicals.
And in terms of supporting better diabetic and prediabetic health, studies have shown some amazing results.
May Support Glycemic Control
Like many of the natural remedies we’ve mentioned so far, bitter melon has been shown to support better blood sugar control.
For example, when type 2 diabetic participants were given a 2 gram dose of bitter melon over 10 weeks, they saw a drop in their A1C levels by an average 0.85%. Another group taking a 4 gram dose saw an even greater drop in A1C of 1.15%.
And as for those with insulin resistance and prediabetes, the influence of bitter melon may be even greater.
Some of the study results include:
- Bitter melon tea was shown to reduce A1c by 63%.
- A small study found that when people ate chopped bitter melon fruit in the morning for 3 weeks, they had a 54% drop in blood sugar levels.
- Even a single 100 mg/kg dose of bitter melon has been observed to help bring blood sugar levels back to normal after a meal!
Bitter Melon May Decrease Your Level of Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is a key contributor to high blood sugar levels. Because when your cells are resistant to insulin, insulin can’t unlock the cells so that glucose can be moved from the bloodstream into the cells.
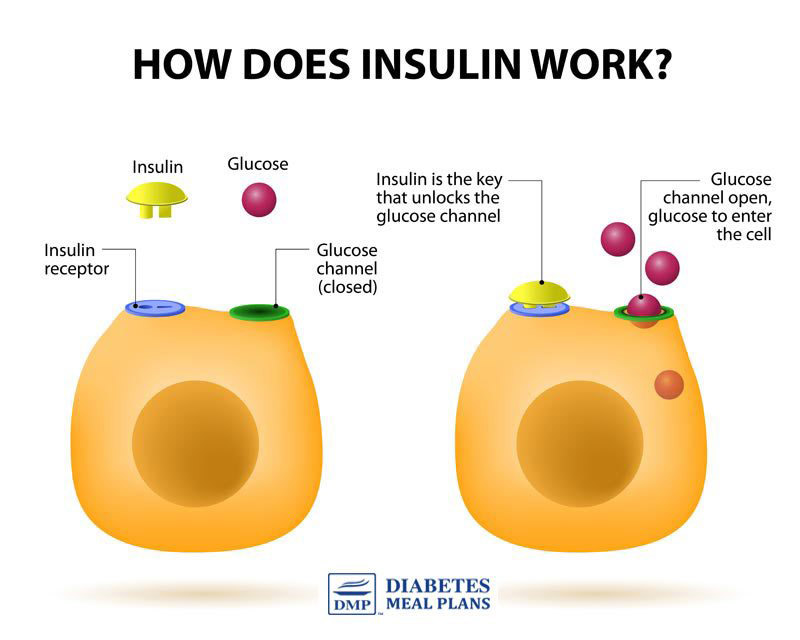
Studies suggest compounds and proteins in bitter melon help to stimulate glucose uptake in insulin resistant cells. It sensitizes the cells so they become more responsive and acts almost like an insulin-substitute to help clear more glucose out of the bloodstream.
On top of that, it may help enhance the function of pancreatic cells to assist with more balanced insulin production.
Ginseng
Ginseng is a flowering plant that comes in 11 different varieties. The root of the ginseng plant is often made into a hot tea and like many of the other herbals discussed here today, ginseng has proven to be effective in aiding with the treatment of diabetes.
May Improve Glucose Tolerance
A review of 8 randomized clinical trials found that ginseng significantly improves fasting glucose and postprandial insulin.
Ginseng supplementation is also associated with an increase in insulin sensitivity.
May Lead to Better Cholesterol Levels
Ginseng intake has been linked to significant improvements in triglycerides, total cholesterol, and LDL levels, as seen in multiple studies.
Mediterranean Culinary Herbs
Rosemary
This herb is a potent anti-inflammatory agent that has been associated with improved metabolic markers such as lower body fat and reduced weight gain, as well as lower levels of glucose, triglycerides, insulin, and various liver enzymes.
Beyond diabetes, rosemary has been found to slow the proliferation and spread of cancer cells and improve neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Oregano & Thyme
Oregano is not only a well-loved culinary herb, but also ranks as one of the top natural antioxidants, along with being a powerful anti-microbial agent. It’s sister, thyme, also exhibits powerful anti-inflammatory properties.
These herbs also protect cell membranes from oxidative damage – and overall this means stronger, healthier cells.

Basil
Basil is a staple herb in the popular Mediterranean diet due to its many disease-fighting properties. It contains various compounds that are anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-viral, and anti-aging!
In terms of inflammation, it both decreases pro-inflammatory molecules while stimulating the production of anti-inflammatory ones. And it’s also been shown to stop LDL cholesterol from oxidizing, which provides superior heart-health protection.
Sage
Sage has been used in folk medicine to treat acute inflammation, menopausal symptoms, and help memory and concentration. And like it’s cousins, it also exerts it’s anti-inflammatory powers on your body’s cells to help improve your health!
Milk Thistle
In type 2 diabetes, the pancreas and insulin are often talked about a lot. But the liver is also extremely important and often overlooked, including in prediabetes where a fatty liver could be promoting insulin resistance.
The liver is involved in many important metabolic functions – blood glucose regulation, cholesterol production and regulation, detoxification, filtering, assimilating and storing nutrients, producing major components of the blood – healthy cells for immunity, energy regulation and hormone production.
Milk thistle promotes improved liver function and liver health, which can have many health benefits for type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
We’ve previously covered milk thistle in detail over here.
Alpha Lipoic Acid
In Germany, researchers and physicians are having great outcomes in treating diabetic neuropathy with alpha lipoic acid.
It’s also shown positive benefits for blood sugar control, cholesterol improvements and may even help with weight loss.
We’ve previously covered alpha lipoic acid in detail over here.
Berberine
Berberine is another very impressive herbal remedy that’s been shown to:
- Lower blood glucose
- Lower A1c
- Lower insulin resistance and improve insulin sensitivity
- Lower cholesterol
- Aid weight loss and reduce weight gain
- Reduce risk of damage from diabetic complications
It’s effect on lowering blood glucose and A1c have even been shown to outperform many common diabetic medications such as Metformin.
We’ve previously covered berberine in detail over here.
Conclusion
There are many herbal remedies for diabetes and prediabetes, ones that have ample scientific evidence to show they work. So if you are to choose one, always choose one that is backed by science.
As for which one to choose, it really depends on your goals as they all have unique benefits.
Follow the links throughout this article to explore more information on the DMP blog, as well as the scientific detail.
As Sarah Outlaw, Clinical Herbalist mentioned above, introduce them one at a time so you can be aware of any sensitivities that may occur.
Be sure to check for any drug interactions if you are currently taking medications. And it’s always advised you check with your physician or healthcare team before taking supplements, too.
Please share this information to help inform others about their choices – thanks!


Hey Jedha, loved this article and although I’ve read about many of these herbs I didn’t know they would also help blood sugar! One you didn’t mention I’ve been exploring lately is olive leaf extract 20%. I haven’t tried it yet but have read it can help with both the production of insulin and insulin reception. It is also a detoxer, so although it has few possible side effects, they say you need to start really slowly.
Looking forward to giving these a cautious try!
Glad you enjoyed it M. We haven’t explored olive leaf extract and diabetes in depth (yet) – thanks for the suggestion! Yes, many herbals are beneficial. But like you say, be cautious and add things one at a time and slowly to evaluate their effects.
Your article is wonderful. I was operated end of August this year with by-pass open heart surgery.
i am taking janoumet one table morning a one evening. my blood sugar level fasting morning is 4.8-5.3 mmol/L. but since 3 days i stopped taking only evening this medicine and i want to cure myself without medicine.
so after stopping this tablet evening my blood sugar morning fasting is 5.6,6 , 6 and today it was 6.3.
i am drinking cinnamom tea morning and evening.
should i continue this test or i must take also evening janoumet.
thank you very much and May God Bless you.
You should always discuss medication questions with your doctor Kamal – it’s never a good idea to just stop taking something without asking first as you do not know the side effects or consequences of doing so.