If you’ve heard of fatty liver and diabetes mentioned in conversation, there’s a good reason – they share an intimate connection.
In fact, study after study suggests there are two things that lead to increased development of fatty liver in people with type 2 diabetes – obesity and uncontrolled A1c levels.
Experts estimate anywhere from 6% to 46% of the general population is affected by fatty liver. As a person with type 2 diabetes, the chances of you having a fatty liver are about 80%!
Your liver is the second largest organ in your body. It filters everything you eat and drink, medications you take, and any toxins you may inadvertently consume. And it is intricately involved in metabolic and hormonal balance.
Fatty liver is a concern because it influences how your metabolism is working, including blood sugar regulation. And if left unchecked, a fatty liver can increase your risk of heart disease.
So what exactly is a fatty liver and what can you do about it? Read on to learn more.
What Is A Fatty Liver?
Non Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease, or NAFLD, is a general term that refers to a build up of fat in your liver. As the name implies, this condition is different from Alcoholic Liver Disease, which is caused by excessive alcohol consumption.
There are two subcategories of NAFLD:
- simple fatty liver – a reversible condition.
- nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, or NASH – the liver cells are inflamed and possibly damaged. This can lead to permanent irreversible liver scarring, also known as cirrhosis, which could potentially lead to liver failure if the damage becomes severe.
People with NAFLD can develop NASH (around 10-25%), although it is not entirely clear why.
Everyone has some fat naturally in their liver. When the weight of fat contained in your liver exceeds 5%, it is considered simple fatty liver. This build up of fat occurs because there is an imbalance between inward and outward flow of fatty acids in the liver. Another way to think of this is that there’s an alteration in the way your body metabolizes fats.
What Are The Risk Factors For A Fatty Liver?
General risk factors for NAFLD include:
- Unhealthy diet
- Higher than normal BMI (or in other words, being overweight or obese)
- Hyperlipidemia (high cholesterol levels)
- Type 2 diabetes (or family history of diabetes) – especially uncontrolled diabetes, for instance, having high A1c levels.
Certain medications can also put you at risk of NAFLD, although this is a much less common risk factor compared to the general risk factors described above.
Please pin, share or tweet; then keep on reading.
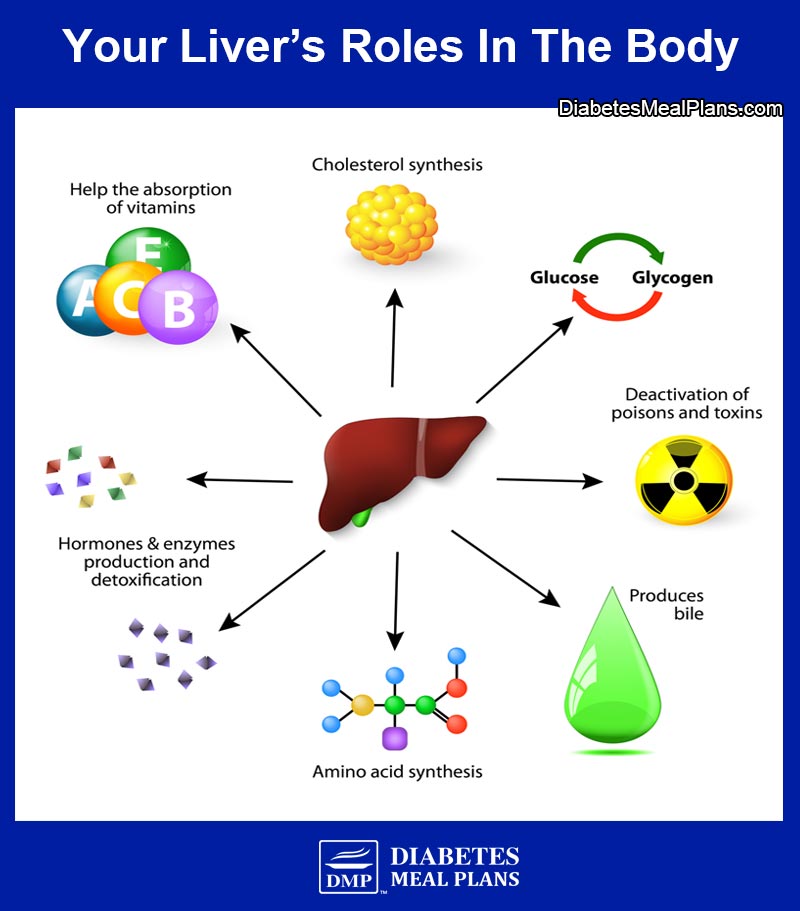
The Connection Between Type 2 Diabetes and Fatty Liver
Due to insulin resistance, people with type 2 diabetes are at a higher risk of developing NAFLD. Changes in hormones such as insulin, along with the presence of insulin resistance, affect enzymes in your body, and this causes an increase in free fatty acids, which can flow into the liver.
Other aspects of metabolism become affected too, such as an increased production of fat formation (called lipogenesis). These factors are promoted by high blood sugar and high insulin levels, which leads to a chain of metabolic events that drive up fat production in the liver. And a cycle can occur where there is an imbalance between inward and outward flow of fatty acids in the liver.
Factors associated with insulin resistance can promote NAFLD, but it also works in reverse, meaning that your fatty liver further promotes insulin resistance. That means doing what you can to reverse and improve liver function, is also very important to your diabetes treatment.
Your diet also plays a key role in the production of excess liver fat.
Your liver cells will convert excess glucose (carbs) into fat. If you’re consuming excess glucose (carbohydrate) and not utilizing it for energy, then the excess will be stored as fat. Some of the fat is stored as abdominal (belly) fat, whereas it can also be stored in other cells including your liver.
Fructose in particular has been shown to increase fat deposits in your liver.
Fructose is:
- a naturally occurring sugar found in fruit
- sugar is 50% fructose
- honey is 50% fructose
- agave is 75-85% fructose
- it is also infamously known as the main constituent of high fructose corn syrup
We encourage all people with diabetes and prediabetes to limit their intake of fructose-containing foods.
What Are The Symptoms Of Fatty Liver?
Most people who have a fatty liver experience no symptoms at all. In fact, even if the condition progresses to NASH or cirrhosis there are rarely noticeable symptoms.
Some people (but very few) may notice a discomfort in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. And jaundice, or yellowing of the eyes and skin, can be a sign of liver cirrhosis.
How Does A Fatty Liver Get Diagnosed?
Since there are relatively few symptoms of NAFLD/ NASH, the diagnosis is often accidental. This means your doctor may bring up concern of NAFLD during routine blood work or an unrelated abdominal imaging study. In some cases a liver biopsy may be warranted as this is the gold standard of diagnosing NAFLD.
Blood Test
One of the first signs of NAFLD is an abnormal liver test identified through blood work. Inflamed liver cells may leak higher-than-normal amounts of transaminase (enzymes) into your bloodstream.
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) are the two enzymes of particular interest. And while both are elevated in NAFLD, you will classically find that ALT exceeds that of AST.
Imaging Studies
Abdominal ultrasounds and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can also aid your doctor in diagnosing NAFLD as fatty liver will show up differently on these scans. Although, imaging studies are unable to differentiate between simple fatty liver disease and NASH.
Liver Biopsy
Your doctor will recommend if he or she feels you need a liver biopsy to diagnosis NAFLD, though, for some people it’s impractical or cost prohibitive to have a biopsy completed.
However, a biopsy can differentiate between NAFLD and NASH. By analyzing the tissue itself, your healthcare team can better assess the amount of inflammation in your liver, the amount of permanently damaged cells, and of course rule out any concern for malignancy (cancer).
NAFLD is not caused by heavy alcohol consumption. In order for a true NAFLD diagnosis, a person must report abstinence or very minimal alcohol consumption (<20g/day).
Please pin, share or tweet; then keep on reading.

8 Proven Ways to Reverse or Prevent Fatty Liver
The good news about all this, is that there is evidence that fatty liver can be prevented and reversed. That’s why it’s imperative to take action as soon as possible, because once permanent damage occurs it cannot be reversed with any intervention.
#1: Intensive Lifestyle Intervention
Research involving over 5000 participants with type 2 diabetes demonstrated that 12 months of intensive lifestyle intervention can result in up to a 50% decrease in liver fat deposits. The intensive intervention included upgrading your nutrition plan with a goal of losing a minimum of 7% of one’s body weight, and completing 175 minutes of exercise weekly.
175 minutes of exercise per week is equivalent to about 30 minutes a day 6 days per week, which is an achievable goal for most people. But if you’re just getting started even 10 minutes a day is worthwhile – any exercise is better than no exercise at all!
#2. Exercise Diversity
Many people tend to focus on aerobic exercise like walking, and evidence proves that aerobic training will certainly help. However, research demonstrates that the benefits of aerobic exercise and resistance training combined lowers liver fat even more, as the exercise diversity targets different metabolic parameters.
If possible, incorporate resistance training 2-3 times per week alongside regular aerobic activities.
Exercise helps the liver burn more fat, makes less new fat, and protects the liver’s cells from damage. It also helps prevent the release of harmful molecules that can cause further damage to the liver’s cells.
#3: Reduce Carbohydrate Intake
Controlling blood glucose levels to promote proper glucose utilization and prevent exacerbation of insulin resistance is another key to success. The best way to achieve better results is to change your diet and nutrition plan.
Based on research, and the success of our members over more than a decade, lowering blood sugar and A1c is more easily achieved by following a low carbohydrate diet.
The reason reducing carbohydrates reduces liver fat is due to that fact that carbs raise blood sugar, which increases circulating insulin in the blood, increasing insulin resistance and fat storage (including fat storage in the liver).
By cutting down on carbohydrate foods, this acts in reverse. You decrease blood sugar, decrease circulating insulin in the blood, decrease insulin resistance and start burning fat from all over the body, including fat that’s accumulated in organs like the liver and pancreas.
Understanding the right carbohydrate foods to choose is critical. Get started today by grabbing a copy of our recommended food list below.
#4: Switch Your Fats
The type of fat (fatty acids) you consume can determine how your body uses them and even where the fat is stored.
All natural fats found in natural whole foods is healthy fat, including fats found in red meat, chicken, lamb, and pork. But there are fatty acids that can help target liver fat directly.
Long chain omega-3 fatty acids are classically known for their anti-inflammatory effects and may be useful in the treatment of NAFLD. A 12-month study found that adding 1 gram of omega 3 fatty acid supplementation improved NAFLD.
Another larger study (2008) also found omega-3s of great benefit to a fatty liver.
The researchers divided participants into two groups:
- group A received 2 grams of omega 3 fatty acid supplement
- group B received a placebo
After 24 weeks of supplementation, 20% of group A was downgraded to zero (no fat in the liver present), compared to just 7% in group B.
Systematic reviews have also confirmed the benefits of omega 3 supplements in targeting liver fat.
If you want to include more omega 3-rich foods, good sources include:
Medium chain triglycerides (MCT) are another type of beneficial fat. MCTs are known to be transported directly into the liver via the hepatic portal vein; this is different to how any other fat is metabolized.
Due to this mechanism, they have been shown to increase fat burning in the liver. Coconut oil is one common source of medium chain triglycerides.
#5: Improve Your Gut Health
Interestingly, researchers have shown that people with simple fatty liver have very different gut bacteria compared to those who progress to NASH (the more severe type of fatty liver disease). This means you can manipulate your gut bacteria to help treat your fatty liver. One way to do this is by encouraging the production of Short Chain Fatty Acids (SCFAs).
SCFAs are produced from fermented fibers in the gut, particularly the large intestine. You can increase SCFAs by increasing your intake of prebiotic fiber-rich foods, such as:
- Asparagus
- Jerusalem artichokes
- Chicory
- Green peas
- Leeks
- Onions
- Shallots
- Spring onions
- Dandelion greens
- Fennel bulb
- Beets
- Cashews
- Garlic
- Pistachio nuts
Probiotic supplements is another plausible natural treatment for NAFLD.
A meta-analysis of studies concluded that probiotics significantly improved liver enzymes ALT and AST, as well as an improving total cholesterol and insulin resistance.
But it gets even better. Research suggests that adding a combo Prebiotic + Probiotic supplement is a powerful way to decrease liver fat and boost liver function, working together to heal the the intestinal barrier!
#6: Get Adequate Vitamin D
Another nutrient intricately related to your metabolism is vitamin D. This vitamin was initially thought to only assist with calcium regulation and bone health, but it is now well known that vitamin D is a key player in your immune health, gut health, reproductive health, and endocrine (blood sugar/ hormonal) function.
As we spoke about earlier, insulin resistance, or metabolic syndrome, is a main risk factor for fatty liver. Research has consistently shown than supplementing with vitamin D can improve insulin sensitivity, and therefore, improve glycemic control (blood sugar regulation).
Furthermore, vitamin D deficiency is commonly associated with NAFLD and studies are beginning to examine the role vitamin D has on NAFLD markers. It has been proposed that vitamin D may play a role in the progression of liver disease. So being that vitamin D deficiency in diabetes is common, it may be wise to discuss your vitamin D status with your doctor and utilize Vitamin D supplementation as needed.
#7: Take Beneficial Supplements To Target Liver Fat
Two final supplements worth noting are milk thistle and apple cider vinegar.
Milk Thistle
Milk thistle (silymarin) has long been known to have amazing health benefits for the liver, including providing anti-inflammatory and antifibrotic properties.

One of the most outstanding things about milk thistle supplementation, is it can actually heal liver damage! So it not only improves overall liver function and directly decrease liver fat, but if there is any damage to the liver, it will help heal it over time.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple Cider Vinegar (ACV) is another natural aide with powerful benefits. According to research, it can help in blood glucose management by improving insulin sensitivity by as much as 34%.
ACV is a natural liver cleanser and helps improve gut bacteria too. Try taking it before meals, it helps lower blood sugar too!
Berberine
Berberine is the best natural therapeutic to replace Metformin, shown to decrease A1c more than Metformin!
It just so happens that it is a fantastic therapeutic for fatty liver as well. Research shows Berberine improves liver enzymes, lipid profiles and insulin sensitivity.
This research demonstrates the powerful influence of Berberine supplements to improve overall liver function.
8. Try Time Restricted Eating
Restricted eating is a type of fasting that limits your eating window to 8-10 hours during the day. There are also other types of fasting such as alternate days or five days eating, two days fasting.
Fasting helps improve fatty liver (NAFLD) by slowing down the liver’s process of making and storing fat. When you fast, your body has less glucose available, so it starts using stored fat for energy. This reduces the buildup of fat in the liver and helps it function better.
Fasting also lowers inflammation and makes the liver less stiff, which means it’s healthier overall. As a result, fasting can reduce the amount of fat stored in the liver, making it an effective way to manage and improve fatty liver disease.
Conclusion
It’s not just your pancreas that’s important to consider in diabetes treatment because your liver is also intricately involved in metabolism and blood sugar regulation. And unfortunately, fatty liver and diabetes often go hand in hand.
The good news is you can prevent or treat fatty liver by making changes to your diet and lifestyle. And adding a few supplements can help too.



Thanks a million. This is, a powerful read with detailed information on fatty liver reversal.
Very informative and helpful article in curbing fatty liver disease. Highly appreciate
Glad you found it helpful! We’ll have more o fatty liver on our podcast soon, so be sure to subscribe!